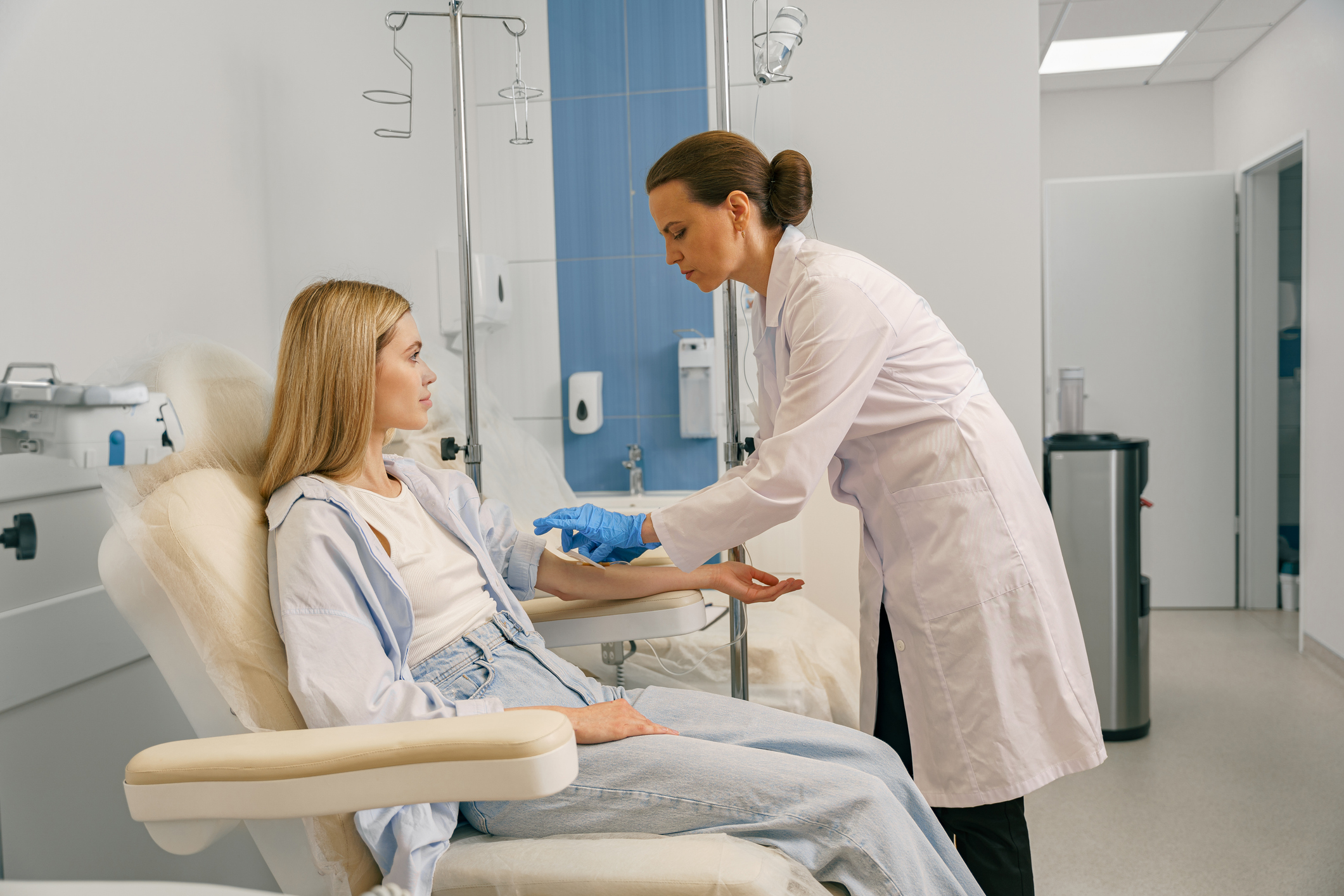
Phlebotomy technicians do more than draw blood. Doctors rely on phlebotomy technicians to assist in making informed treatment decisions, and each step in the process requires focus and accuracy. Whether your state requires certification or not, getting certified is an important way to build confidence in yourself, your employers, and your patients. So, what does a phlebotomy technician do?
What Does a Phlebotomy Technician Do?
Here is a review of the most common duties of a phlebotomy technician:
Preparing the Work Area and Equipment
Before seeing a patient, phlebotomy technicians prepare the necessary instruments to draw blood. This includes drawing needles, tourniquets to help veins show, alcohol or iodine swabs for cleaning, blood collection tubes and labels, gloves, gauze, and bandages. For example, if a doctor orders a complete blood count (CBC), the phlebotomist must select the correct lavender top tube and gently invert it after drawing blood to prevent clotting.
Verifying Patient Identity and Test Orders
Phlebotomists are responsible for confirming they have the right patient. They usually request at least two identifiers, such as full name and date of birth, and verify that information against the lab order. For example, a fasting glucose test drawn from a patient who just ate lunch may need to be rescheduled. The phlebotomist must catch this before drawing the blood.
Explaining the Procedure and Gaining Consent
Phlebotomy technicians must clearly explain the process and answer any questions. They also ease patient fears. Many people are nervous around needles, and a calm explanation helps reduce anxiety.
Performing the Blood Draw (Venipuncture or Fingerstick)
This is the most critical task. The phlebotomist must select the best vein, insert the needle smoothly, draw the correct amount of blood, monitor the patient’s response, and then remove the needle, apply gauze, and secure the site with a bandage. A phlebotomy technician drawing from an elderly patient with fragile veins may need to use a smaller butterfly needle and work more slowly to avoid bruising.
Labeling and Handling Blood Samples
Once the blood is drawn, it must be labeled correctly before the patient leaves the facility. Each label includes the patient’s name, date of birth, time of collection, and test code or barcode. Improper labels can lead to delayed test results, misdiagnosis, or a need for retesting. Phlebotomists then store the samples properly; some require refrigeration, while others must be processed quickly.
Entering Data and Completing Documentation
Certified phlebotomy technicians often enter patient and sample details into electronic medical records or lab systems. Accuracy is important to avoid data errors. If a patient faints after the draw, the technician must report the incident, complete the necessary paperwork, and alert the nurse or provider.
Following Infection Control and Safety Rules
Phlebotomists must adhere to strict safety protocols at all times. This includes wearing gloves, using sharps containers for needle disposal, cleaning surfaces between patients, and following protocols for exposure to blood. This protects both the worker and the patient from disease.
Where Do Certified Phlebotomy Technicians Work?
Phlebotomy technicians are in high demand. Their skills are used wherever blood tests, donations, or lab work are required. Each workplace has its own pace and patient types. Some of the work environments that a certified phlebotomy technician will work in include:
Hospitals
Hospitals are among the most common settings for phlebotomy technicians. These extensive facilities often have 24-hour labs. Phlebotomy technicians in hospitals draw blood from patients in emergency rooms, intensive care units, and general floors.
Outpatient Clinics and Doctor’s Offices
In outpatient clinics, the pace is slower and more routine. Patients visit for check-ups, monitoring of chronic conditions, or wellness screenings. Phlebotomists typically work Monday through Friday in outpatient clinics and doctors’ offices. For example, a phlebotomist in a diabetes clinic may draw blood for A1C tests to monitor long-term blood sugar levels.
Diagnostic and Reference Laboratories
Many samples from doctor’s offices are sent to outside labs for testing. These labs employ phlebotomists to collect blood, process specimens, and prepare them for testing. At a national lab chain like LabCorp or Quest Diagnostics, a phlebotomist may see dozens of patients per day with a wide range of test orders.
Blood Donation Centers
Donation centers focus on collecting blood, plasma, or platelets from healthy donors. Phlebotomists in these centers draw larger volumes of blood and monitor donors throughout the process. A phlebotomy technician at a blood center may assist with mobile blood drives, guiding donors through the entire donation process and monitoring for potential side effects, such as dizziness.
Urgent Care Centers
Phlebotomy technicians in urgent care assist doctors in diagnosing illnesses quickly. They often collect blood for flu tests, disease detection, strep screens, or basic labs for infections and injuries. A patient with chest pain may visit an urgent care facility, where a phlebotomist draws blood for a heart enzyme test.
Long-Term Care and Rehabilitation Facilities
Nursing homes and rehab centers often have phlebotomists come in to collect blood for routine monitoring. Some facilities have in-house staff, while others rely on mobile services.
How to Become a Certified Phlebotomy Technician
Phlebotomy technicians collect blood for testing, donation, and research. Certification is often required to work in this role. Here’s how you can become certified, step by step:
Step 1: Earn a High School Diploma or GED
Before you can train as a phlebotomist, you’ll need a high school diploma or equivalent. Most programs, including CyberTex, require this before enrollment.
Step 2: Enroll in the Medical Assistant Program at CyberTex
CyberTex offers a Medical Assistant program that includes phlebotomy training. This is a hands-on way to build skills while also learning other in-demand clinical tasks. At CyberTex, you’ll learn:
- Venipuncture (drawing blood)
- Safety and infection control
- Patient communication
- Specimen labeling and handling
- Basic lab procedures
Step 3: Complete Clinical Practice
During your program at CyberTex, you’ll complete real-world training in a clinical setting. This provides you with the opportunity to practice drawing blood from actual patients, work under the supervision of experienced medical staff, and learn to handle challenging veins or manage nervous patients.
Step 4: Graduate from the Program
Once you complete all classes, labs, and clinical hours, you’ll graduate from the Medical Assistant program. You’ll now be ready to apply for certification. Graduates are eligible to sit for exams offered by national certification agencies.
Step 5: Apply for a Phlebotomy Certification Exam
Several national groups offer phlebotomy technician certification. CyberTex graduates may be eligible to take the Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT) exam through the National Healthcareer Association (NHA).
Step 6: Start Applying for Jobs
After certification, you can apply for phlebotomy jobs. Your CyberTex training, combined with certification, makes you a strong candidate for entry-level employment. Additionally, the career services at CyberTex will help match you with job opportunities that align with your passion and skill set.
Want to Learn More?
The Medical Assistant Training Program at CyberTex Institute of Technology prepares you for the CCMA from the National Healthcare Association. The curriculum is centered around the knowledge and skills you will need when you take the CCMA exam.
At CyberTex, we take excellent care of you by providing hands-on training, practical experience, and the support it takes to get started in a medical assisting career without spending years in school. You will learn clinical and clerical skills and prepare to work in physician’s offices, hospitals, and other medical facilities.
Contact us today to learn more about our Austin and Killeen campuses.